Assessment of Barrier Damage of Adhesive Dressings after Repeated Applications and Removal
Source: proDERM Institute for Applied Dermatological Research, Schenefeld/Hamburg, Germany. Study no. 14.0364-23
Strength
Peel force on skin [N/20mm]
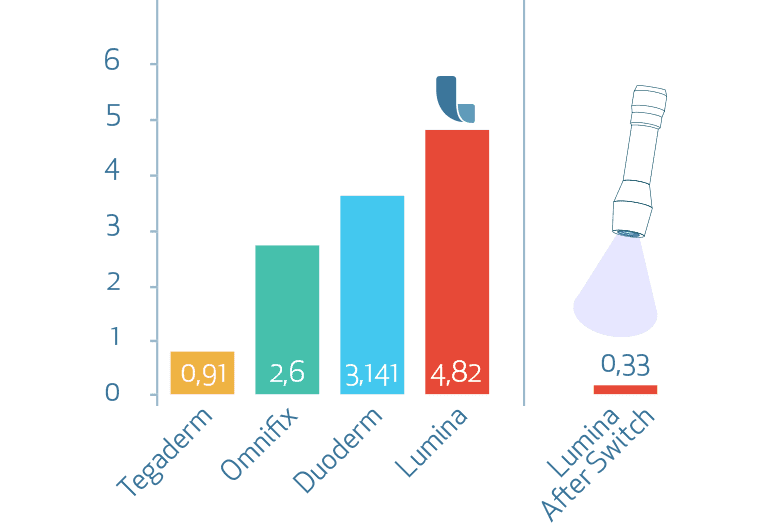
Pain
Pain on Visual Analog Scale (VAS)
Damage
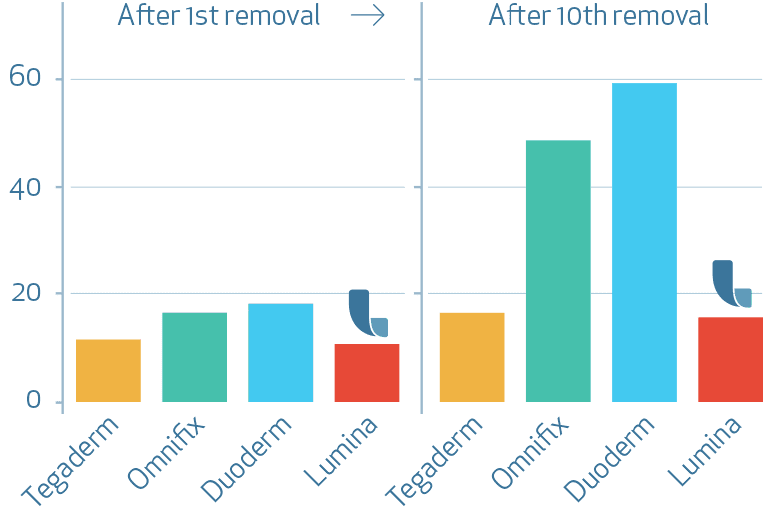
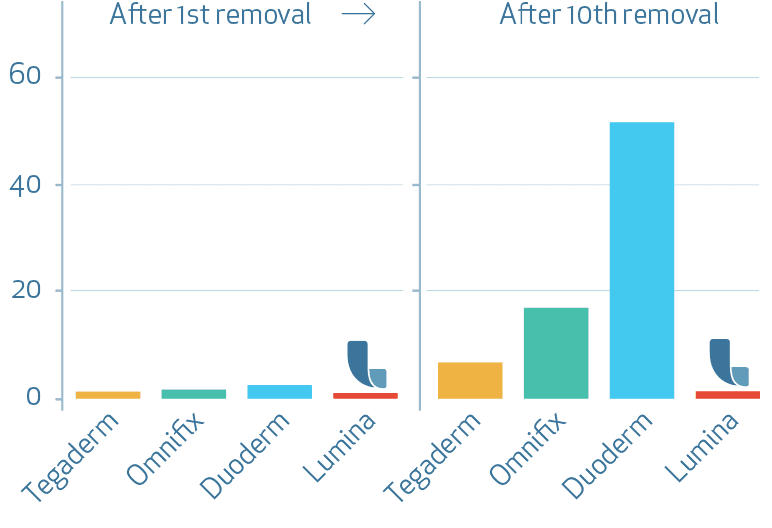
Skin damage increase TEWL [g/(m2h)]
Conclusion
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the skin barrier damage by Transepidermal Water Loss (TEWL) as well as the pain during removal assessed after repeated removal of the four adhesive dressings Tegaderm (A), Omnifix (B), Duoderm extra thin (C) and LUMINA FILM (D).
Therefore 10 repeated applications were performed and TEWL measurements were done before product application as well as after 2, 4, 6, 8, 9 and 10 applications and removals. Additionally the subjects assessed the extent of pain during removal of the dressings after 1, 4, 6, 8 and 10 applications and removals. The test product LUMINA FILM (D) was exposed to UVA-light 365 nm before removing.
Transepidermal Water Loss (TEWL) increased over time of repeated application and removal of the dressings for all tested products. The highest mean value and therefore strongest barrier damage was found for the test product Duoderm extra thin (C) followed by test products Omnifix (B), Tegaderm (A) and finally LUMINA FILM (D). Comparisons of the assessment times to Baseline measurements performed for test product LUMINA FILM (D) showed slightly but significantly increased TEWL values compared to baseline after 6, 8, 9 and 10 applications and removals. However the mean values indicate no clear barrier damage for test product LUMINA FILM (D).
Compared to all test products product LUMINA FILM (D) led to the smallest increase of TEWL at the end of the study.
Regarding the subjects’ assessment of pain during removal of the dressings the subjects noted significantly less pain removing test product LUMINA FILM (D) compared to test products Omnifix (B) and Duoderm extra thin (C) after 4, 6, 8 and 10 applications and removals. Compared to test product Tegaderm (A) the test product LUMINA FILM (D) was found to be superior, thought the result was not significant at all assessment times.
In this study LUMINA FILM (D) performed best concerning conservation of barrier intactness and pain avoidance at peel off in a test design of 10 times repeated dressing application and removal.
Patient Studies
Three studies of 50 patients (150 in total) were conducted in Germany making use of Lumina’s post-op and film dressings. The studies focused on the usability of dressings with switchable adhesive in a clinical setting and the use of the Switch Torch. The results show that both user and patient would use the product again.

1. SWITCHABLE FILMDRESSING AND NPWT
The study was initiated to evaluate if the switchable formulation of the adhesive ensures a durable and effective occlusion of the dressing and function of NPWT. Also that the defined adhesion is in the range of patient and user satisfaction.
PRODUCTS USED:Film dressings 140 & 141 (acrylic)Switch lamp 1000520
Schmitz M, Pilot-Study Switchable Film Dressing and NPWT: A non-interventional, non-placebo-controlled, national pilot study, Wound Medicine (2019)

2. SWITCHABLEPOST-OP DRESSING
The study evaluated suitability for use, as well as user and patient satisfaction during the use of the tested postoperative dressings for the use on postsurgical wounds for routine wound care.
PRODUCTS USED:Post-op dressings 409 & 410 (PU)Switch lamp 1000520
Schmitz M, Pilot-Study Switchable Post-Op Dressing:
A non-interventional, non-placebo-controlled,
national pilot study

3. SWITCHABLE DRESSINGS ON ELDERLY SKIN WITH CHRONIC WOUNDS
The study evaluated suitability for use, as well as user and patient satisfaction during the use of the tested postoperative dressings for the use
on postsurgical wounds for routine wound care.
PRODUCTS USED:Film dressings 411 & 412 (PU)Post-op dressings 409 & 410 (PU)Switch lamp 1000520
This study evaluated the suitability of using switchable dressings as well as user and patient satisfaction. The included patients were elderly with chronic wounds.
The Results
The results show that both user and patient would use the product again.
FIRST VISIT
SECOND VISIT
THIRD VISIT
0=insufficient, 100=very good
FIRST VISIT
SECOND VISIT
THIRD VISIT
0=insufficient, 100=very good
FIRST VISIT
SECOND VISIT
THIRD VISIT
0=insufficient, 100=very good